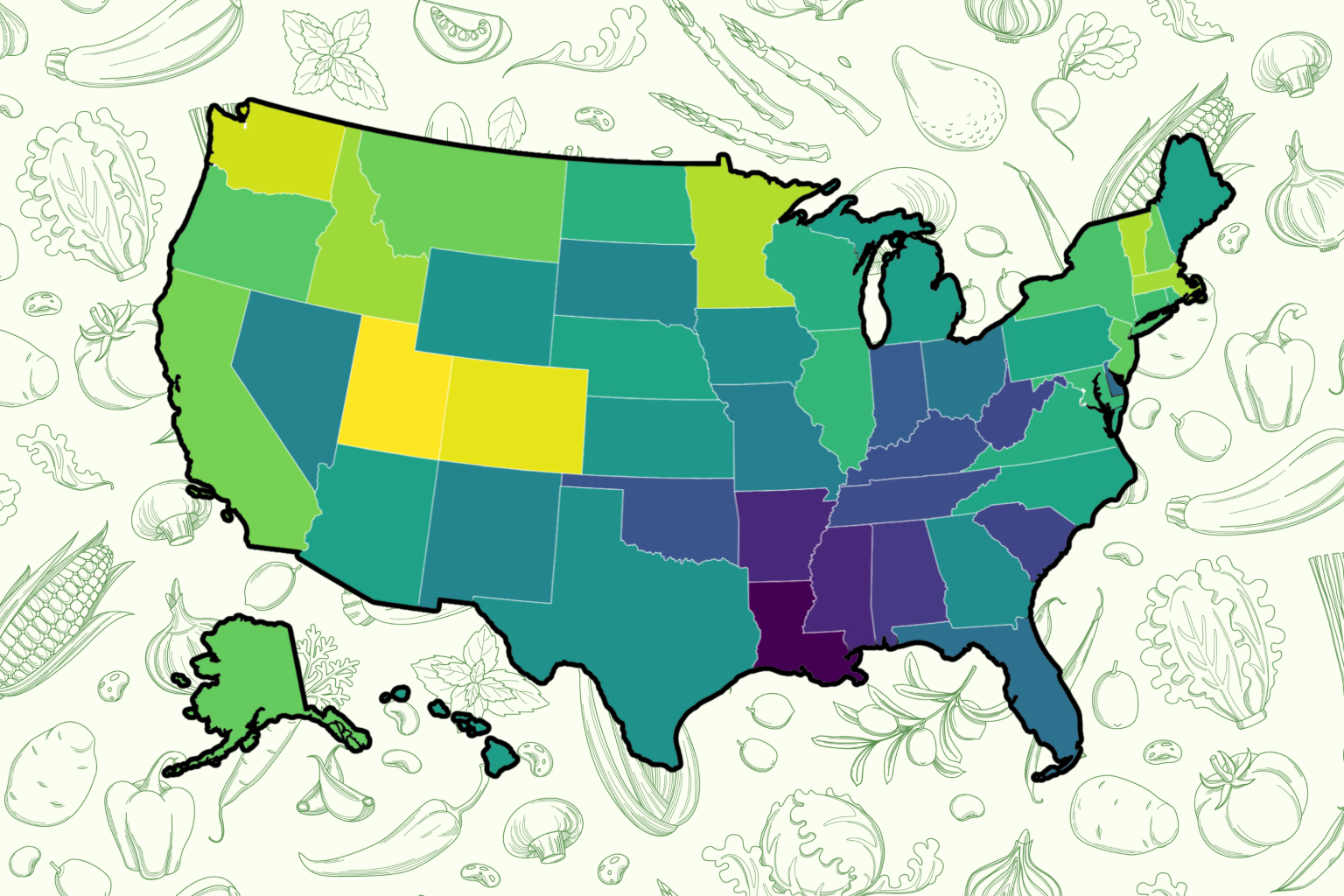
A recent report by Trace One, a product lifecycle management company, has revealed significant disparities in dietary habits across the United States, highlighting Utah as the state with the healthiest diet. The report, which assigned a “Healthy Diet Index” to each state based on nine factors, utilized data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Department of Agriculture to assess metrics such as daily fruit and vegetable consumption, alcohol and sugar-sweetened beverage intake, food insecurity prevalence, and the incidence of diet-related health problems like obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. The analysis revealed a clear geographic pattern, with Mountain West and Northeast states generally exhibiting healthier dietary habits compared to Southern states, which consistently ranked lower in the index.
Utah’s top ranking stemmed from a confluence of positive dietary factors. Residents reported high levels of fruit consumption, low consumption of sugary drinks, and notably lower rates of diet-related health conditions. Colorado secured the second position, boasting the lowest obesity rates in the nation, coupled with high fruit and vegetable intake, low diabetes and chronic disease prevalence, and reduced levels of food insecurity. Washington followed closely in third place, exhibiting strong performance across most metrics, with the exception of slightly elevated alcohol consumption. Rounding out the top ten were Minnesota, Vermont, Massachusetts, Idaho, California, Montana, and New Hampshire, reflecting a concentration of healthy dietary practices in the Northeast and Mountain West regions.
In stark contrast, nine out of the ten lowest-ranking states hailed from the South, underscoring significant dietary challenges in this region. Louisiana, Arkansas, and Mississippi occupied the bottom three positions, burdened by high rates of food insecurity, a key factor contributing to unhealthy eating habits. These states exhibited food insecurity rates significantly higher than the national average of 12.2%, with Arkansas reaching 18.9%, Texas at 16.9%, and both Mississippi and Louisiana at 16.2%. The report attributed this disparity to the limited access to affordable and nutritious food options for lower-income families, forcing them to rely on cheaper, calorie-dense alternatives. This highlights the complex interplay of socioeconomic factors and dietary health, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to improve access to healthy food in these vulnerable communities.
Further analysis of specific dietary indicators revealed notable regional variations. New Hampshire stood out with the lowest food insecurity rate in the nation at 7.4%, while New England states generally excelled in fruit and vegetable consumption, with over 64% of adults reporting daily fruit intake and over 84% consuming vegetables daily. Vermont recorded daily fruit consumption among 66% of its adult population, while Maine led the nation in vegetable consumption with an impressive 87% of adults eating vegetables every day. These findings suggest a strong correlation between food security and healthy eating habits, reinforcing the importance of addressing food insecurity as a critical step towards improving overall dietary health.
The prevalence of overweight and obesity also showed distinct geographic patterns, concentrating primarily in Southern and Midwestern states. West Virginia recorded the highest rate at 73.2%, followed closely by Iowa at 72.1% and Louisiana at 72%. Conversely, Colorado and Hawaii exhibited significantly lower rates at 59.8% and 60.5% respectively, highlighting the influence of regional factors on weight management. Similarly, diabetes prevalence followed a similar trend, with West Virginia again topping the list at 18.2%, followed by Mississippi at 17% and Louisiana at 16.1%. In contrast, Utah, Colorado, and Alaska reported the lowest diabetes rates at 7.8%, 8.6%, and 8.7% respectively, suggesting a potential link between healthier dietary habits and lower chronic disease prevalence.
The Trace One report provides valuable insights into the diverse landscape of dietary habits across the United States. By highlighting the states excelling in healthy eating and those facing significant challenges, the report underscores the need for targeted interventions to improve dietary health nationwide. Addressing food insecurity, promoting access to affordable and nutritious food options, and encouraging healthier eating habits are crucial steps towards reducing the burden of diet-related diseases and improving overall public health. The stark regional disparities revealed in the report call for a multi-faceted approach involving policymakers, healthcare providers, and community organizations to create sustainable solutions for promoting healthy diets across all communities.