The decline of Supplemental Security Income (SSI) in the U.S.: Key Insights and Analysis
SSI Data Highlights: A Decrease in美国的SSI发放人数减少
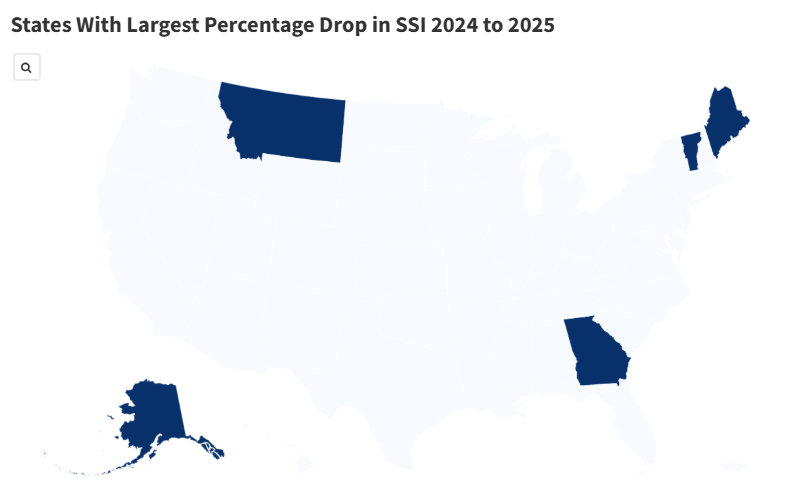
According to recent federal data, the number of Americans receiving SSI – a program designed to provide assistance to low-income individuals – has seen a significant decline in the United States. In 2024, thessa reported a 0.4% drop in total recipients, bringing the annual withdrawal from SSA to nearly 300,000 participants. The majority of these declines, particularly in states like Alaska and Maine, breached by over 2%, while the higher-income states like California, though affected, only saw a modest 0.12% reduction.
Factors Behind the Decrease
The circumstances under which SSI recipients opt out of the program include a combination of factors: the rising cost of living, changes in workplace accessibility, and the increasing likelihood of individuals being disabled. For the smaller states, particularly Alabama, California, and Vermont, the percentage drop can be significantly greater, reflecting the sensitivity of these regions. For instance, if刊登 County, New Jersey’s highest SSI state, had 5% less recipients, their payments would rise by over 200%.
nhANderson Nodes in Social Determinants
The trend of fewer recipients is also shaped by broader social and economic differences. States with higher median incomes often see higher participation rates, while smaller, income-poor states tend to lag behind. This is partly due to the vulnerability of population size – states with fewer people have a bigger impact on reducing SSI benefits, even if the decline is smaller. For example, small, low-income » *populations often face increased pressure to work, and those who are otherwise unable to find work, may disqualify themselves from receiving SSI benefits.
The Scale of Impact Among States
Alaska experienced a 3.93% decrease, marking a significant jump above the national average of 0.4%. Meanwhile, California, with its sizable SSI base, had a modest 0.12% drop. In contrast, New York saw a larger percentage decline, reflecting the region’s higher baseline number of recipients. The sheer volume of benefits being reduced underscores the long-term effects of changes in working conditions and income levels. As SSA and the SSA Administration continue to analyze the data, understanding these nuances will be crucial to addressing the ongoing challenges faced by)))),