AI-Powered Breast MRI Screening: A Breakthrough in Healthcare Screening
The rapidly evolving field of healthcare technology has seen groundbreaking innovations in diagnostics, each addressing the limitations of traditional methods. At the University of Washington, Microsoft’s AI for Good Lab, and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, researchers have developed a novel AI tool that significantly enhances breast MRI screening. This system, known as the AI for Anomaly Detection, represents a pivotal step in the democratization of mammography and cancer detection.
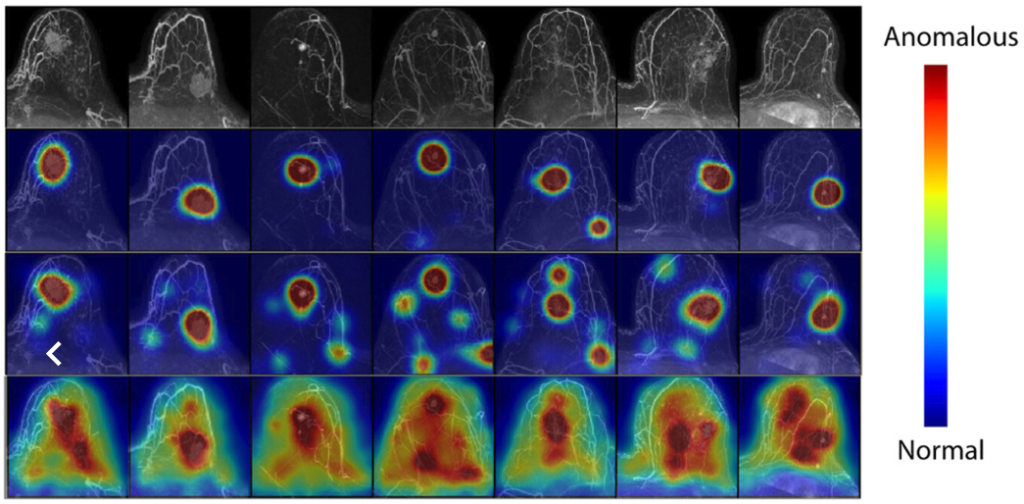
The innovation behind this system lies in its unique approach to identifying abnormalities in MRI scans. Unlike conventional AI models, which typically flag cancer by detecting positive images, this new tool reverses the process. By learning to recognize normal, benign tissue, the system can flag anomalies one pixel at a time. This anomaly detection approach not only improves sensitivity but also provides precise information about where suspicious tissue is located.
Developed in collaboration with leading researchers, the AI was trained on over 9,500 breast MRI scans, spanning a 12-year period from 2005 to 2022. The study’s findings have been published in a prominent journal within the field, solidifying its significance. The researchers’ extensive dataset provided the foundation for the model’s ability to distinguish between normal and abnormal tissue at the pixel level.
The anomaly detection approach has a direct impact on clinical practice. Unlike current diagnostic tools that often report whether cancer has been detected, this system goes a step further, highlighting the exact area of concern. This level of detail enables radiologists to prioritize further diagnostics and guide medical commons more efficiently, ultimately improving the accuracy and comprehensiveness of cancer screening programs.
The significance of this breakthrough extends beyond the medical community. By enabling more accurate and extensive screening, the AI model could transform how breast cancer is diagnosed. Currently, mammography is a dominant screening tool, particularly in high-risk populations, but its cost and verification speed have been criticized. The new system offers a potential pathway to expand breast MRI screening to more women, addressing significant disparities in healthcare access.
However, the model’s capabilities are not without hurdles. Early adoption faces technological and clinical challenges, such as limited understanding of how AI produces its flagged areas. As a result, the team is working on additional studies to validate the system’s accuracy and effectiveness. This cautionary progression underscores the need for continuous improvement and trust, ensuring that the tool aligns with the expertise of radiologists.
In summary, the University of Washington, Microsoft’s AI for Good Lab, and Seattle’s Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center researchers have established a revolutionary tool in the field of healthcare: the AI for Anomaly Detection. This system enhances breast MRI screening by offering more accurate and detailed information than current methods. Its adoption has the potential to expand access to cancer detection, particularly in underserved populations, by providing a more reliable and efficient diagnostic approach. As demonstrated by the research’s findings, this breakthrough could revolutionize how breast cancer is diagnosed and managed, ultimately improving patient outcomes.