Certainly! Here’s a summary of the provided text, condensed into six paragraphs:
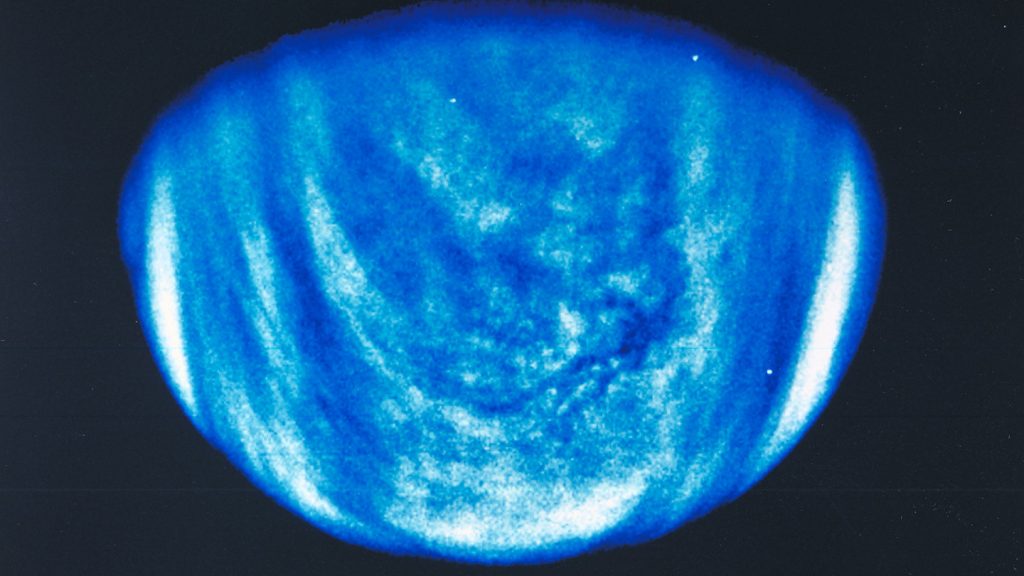
Introduction to the Quest for Life on Venus
[Pt. 74, BOSTON] Researchers are exploring a novel device designed to collect droplets of sulfuric acid, a byproduct of Venus’ sulfuric acid atmosphere, and send them back to Earth for analysis of potentially life-starter molecules. This effort aims to shed light on the potential for life on this hot,———
Planet, supported by Iaroslav Iakubivskyi and his team, who describe how sulfuric acid may serve as a solvent for life-essential molecules, counteracting its long-held belief as a "sterile plasma." Their findings could help scientists understand how life might arise on Venus.
Venus’ Sweetfuture for New Discoveries
In the past few years, Iakubivskyi and his research group have claimed that sulfuric acid can theoretically support organic chemistry needed for stable nucleic acids and amino acids. Together, these data suggest that sulfuric acid could serve as a solvent, rather than an disruptive force, for life, particularly on Venus. "Rather than being disruptive, it might actually be a promising route for lifeoders," he said. Their results indicate that Venus offers a unique potential for life, though further exploration is needed to confirm these findings experimentally.
The Ongoing内蒙古 mission
The researchers developed a prototype device called "Cloud Catcher," made from four layers of wire mesh capable of attracting atmospheric droplets. russe lab partners with space firm Rocket Lab to execute the Morning Star Missions, which aim to send samples of Venus’ atmosphere to Earth. The first probe will travel to Venus and measure sulfuric acid droplets under controlled conditions.
The Promise of Progress
The mission reflects the greater vision NASA and the European Space Agency share regarding exploration. They plan to launch spacecraft to Venus within the next decade andons ongoing efforts to understand Venus’ unique chemistry. This collaboration not only seeks to advance Earth’s understanding of the solar system but also opens possibilities for new discoveries on Venus itself.
Implications for Life and Exoplanet Research
Iakubivskyi emphasized the significance of Venus as a potential host for Earth-like life. While limited to its atmosphere, the findings of this device could advance our understanding of atmospheric chemistry and serve as a transcendence point for future alien colonization efforts. The story of Venus will continue to shape the field of exoplanet research, much like Earth’s vibrant ecosystems have inspired the exploration of other worlds.
The Final Step: Launch the Massacre
The researchers’ findings, while largely theoretical, represent a critical step toward answering fundamental questions about life and planetary atmospheres. As Iakubivskyi notes, "this is proof of a new era." The successful execution of the Morning Star mission could pave the way for embracing the science of-tokenhts and paving the way for new discoveries on Venus and beyond. Together, these efforts are redefining the possibilities for life and the solar system.