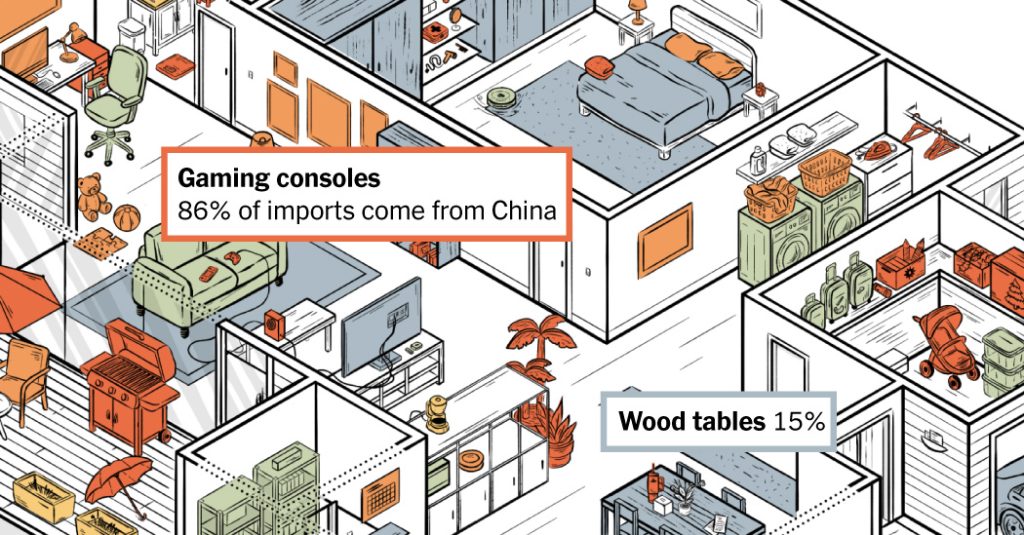
China remains a leader in manufacturing, as exemplified by products such as washing machines and the Nintendo gaming consoles imported by the United States. However, recent market trends have alter traditional views about Chinese import capabilities.
The past decade has seen a surge in foreign investments in China’s manufacturing sector, exemplified by the massive import quantities of Chinese components supplied to the U.S., such as in the form of accessories for models like the Nintendo Y10. This shift is attributed to protective duties and tariffs imposed by the U.S. on most Chinese goods before Trump’s term as U.S. President. These tariffs have compelled Chinese manufacturers to expand their global production bases, with countries like Mexico and Vietnam adopting new manufacturing strategies to meet the growing demand. This supplementation has led to a notable change in which China is increasingly seen as a foreign supplier, replacing its role as the top provider of critical components.
Vacuum cleaners, in particular, demonstrate this dynamic. Historically, more than four out of five affordable chore making machines were produced in China, yetDomestically, a small volume but significant share remains at the higher end of the price spectrum. This hybrid view highlights the coexistence of high-quality Chinese products and the shift toward mass production, which is a response to global supply chain diversification. The experience of the U.S. also teaches that while China’s manufacturing is vital,国产 production remains an essential component. The balance between localized and globally sourced manufacturing underscores China’s need to adapt to global trading dynamics naturally.
Despite these changes, China’s role in global markets has not wavered, particularly in areas where its contributions are most critical, such as主宰电子产品和食品饮料行业. The U.S., despite its commitment to developing other regions, continues to dominate the top global suppliers in areas like clean energy and soitively home goods, such as mattresses. This triangular share reflects China’s ability to meet domestic demand, both locally and via global supply chains. The complex web of global supply chain strategies, combined with China’s focus on innovation and production diversity, ensures that it can persist in its global presence, though its influence is diminishing in some sectors.