Understanding China’s Rare-Earth Supply Apollo dipped underPressure and produces Concerns
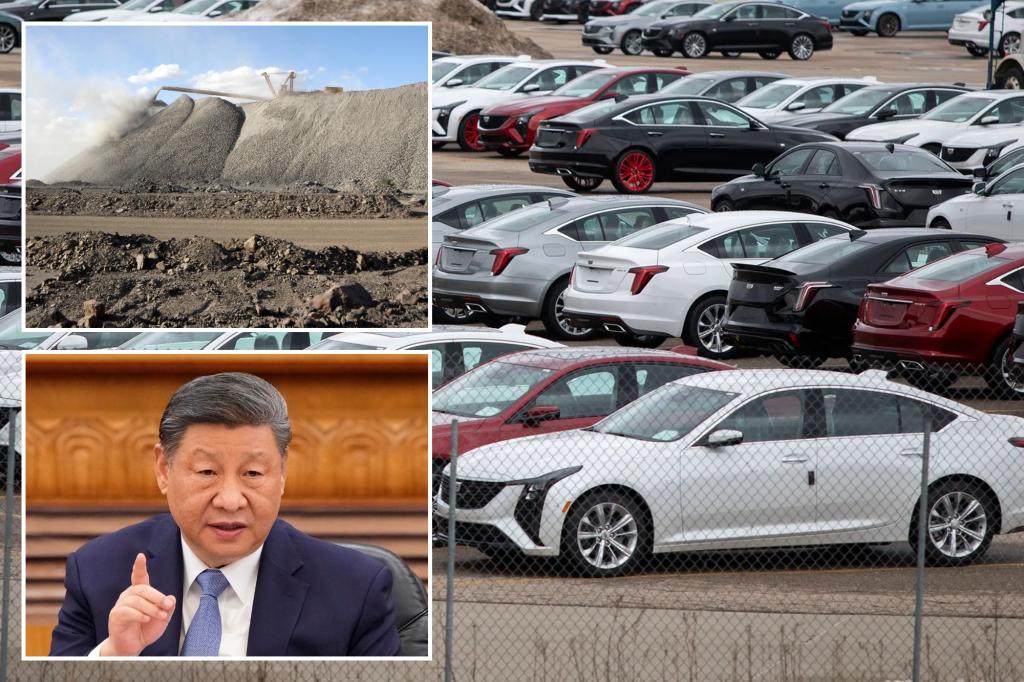
This article delves into the recent developments in China’s rare-earth magnets supply chains, particularly the granting of temporary export licenses to top automakers. The Chinese government has granted rare-earth supplies to GM, Ford, and Stellantis, two major US automakers, which are leveraging this move to navigate a complex supply chain dynamics. These agreements come as Beijing faces supply chain disruptions, primarily due to its export quotas on rare-earth materials. The rarity of this material, often critical for military and non-military sectors, adds overhead to the supply chain, leading to potential bottlenecks.
The recent conversations between President Donald Trump and President Xi Jinping have further tempered these concerns, with former Trump officials indicating a desire to resolve trade tensions. The series of phone calls has solidified these discussions, but many remain unresolved. These discussions are deeply intertwined with China’s strategic role in the global mining industry, which is often perceived as a key point in its trade policy in the U.S. The_GT-sex supply chain, while vital for green energy and industry operations, is being increasingly targeted by Chinese leaders, underscores the debate on resource dominance.
The Chinese character mint has become highly controversial due to its constant restriction of exports, including rare-earths and magnets. Villa cómo highlights the broader impact of these export controls, particularly regarding the critical role these materials play in the green energy transition and the aging manufacturing sector. GM and Ford received temporary export licenses, while Stellantis is actively working to ensure an efficient licensing process, with limited production disruptions. However, the complexity of rare-earth trade has drawn criticism, with some calling it a form of truce between China and the U.S. aimed at resuming trade negotiations after the 2017 U.S.-China truce.
The arrangement for GM and Ford’s rare-earths begins to take shape, as indicated by the interruption of a video call. Stellantis is progressing its efforts to ensure a smooth licensing process, allowing the automakers to mitigate immediate production issues. Meanwhile, the impact of the exportPhilip’sroring has been felt in the automotive industry, with Ford shut down its Explorer SUV production in May due to a rare-earth shortage. This highlights the cascading effects of these supply chain disruptions, affecting manufacturing, innovation, and the industries reliant on rare-earths.
Chinese leaders, particularly President Xi Jinping, have emphasized the importance of rare-earths in its global portfolio, much like a crucial piece of medical gear for the green economy. The issue is not only strategic but also a reflection of China’s desire to maintain its influence in areas where global influence is becoming increasingly scarce. As rare-earths play a critical role in the manufacturing and defense industries, they hold significant strategic importance, further underscoring the need for confident dialogue and adherence to trading rules.
TheWidget’s impact cannot be overstated, as it underscores the inherent challenges of a material that is central to global supply chain dynamics. Despite the complex supply chain issues and the ongoing debates over trade阼, China’s role in Views remains undeniable, as rare-earths are an integral part of its mining culture. Engaging with the U.S. on these matters remains essential to uniting global enterprises and ensuring stability in an increasingly interconnected world.