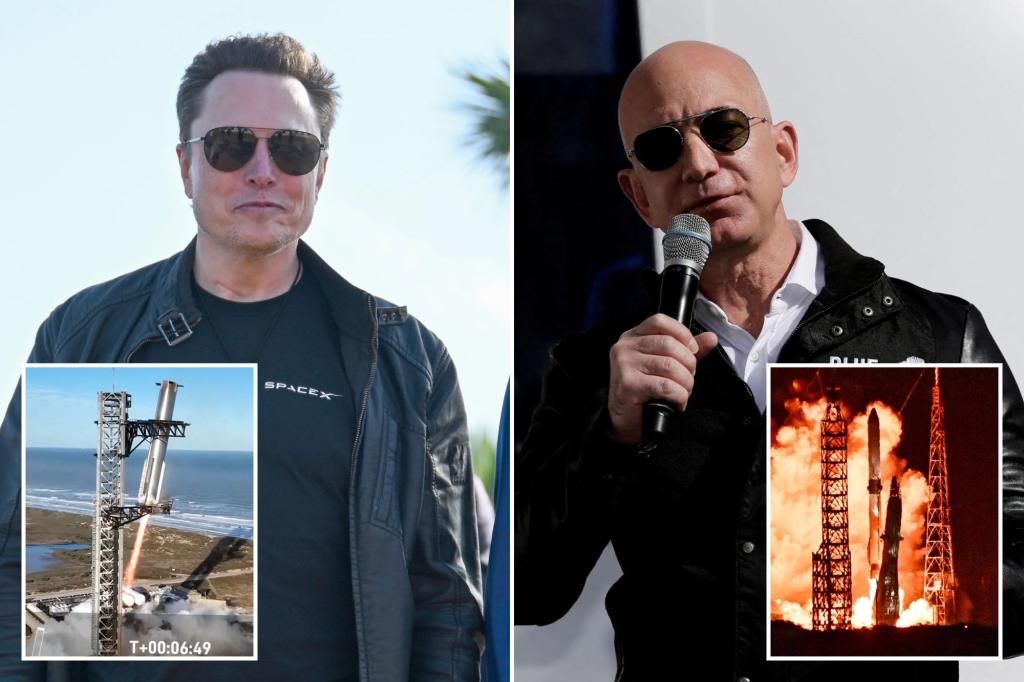
The dawn of a new space race broke on a Thursday morning in early 2025, not between nations, but between two American titans of industry: Jeff Bezos and Elon Musk. Bezos’ Blue Origin achieved a remarkable feat, successfully launching its New Glenn orbital-class rocket on its maiden voyage. This marked a significant milestone for the company, establishing it as a legitimate competitor in the private space industry. Just hours later, Musk’s SpaceX, already a dominant force in the field, launched its Starship rocket, further intensifying the competition between the two billionaires. While both launches were deemed successful, neither fully achieved their objectives, with Blue Origin losing a rocket booster and SpaceX losing its Starship craft. This head-to-head competition signaled a new era in space exploration, driven by private enterprise and fueled by the ambitions of these two exceptionally wealthy individuals.
The rivalry between Bezos and Musk, both described as driven by substantial egos, is palpable. Musk, with SpaceX’s impressive launch record of 138 launches in 2024 compared to Blue Origin’s four, held a clear lead in the race. However, Blue Origin’s successful orbital launch was a significant achievement, considering the immense technical and financial challenges involved in the space industry. The costs associated with these endeavors are astronomical, with New Glenn’s development exceeding $2.5 billion and each launch costing around $68 million. SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy launches also carry a hefty price tag of approximately $90 million per launch. Despite the competition, a sense of mutual respect existed, with Musk publicly congratulating Bezos on Blue Origin’s achievement. This acknowledgement underscored the magnitude of the accomplishment and the shared ambition to advance space exploration.
The lucrative potential of space-based industries, particularly satellite deployment, is a driving force behind this new space race. With a backlog of satellites awaiting launch, the demand for reliable and cost-effective launch services is immense. Both Blue Origin’s New Glenn and SpaceX’s Starship are designed to address this demand, capable of transporting heavy payloads into orbit. This competitive landscape is beneficial for the industry, fostering innovation and potentially driving down launch costs in the long run. The entry of Blue Origin as a serious contender challenged SpaceX’s dominance, creating a more dynamic and competitive market. This competition promised to accelerate the pace of space exploration and development.
Adding an intriguing layer to this rivalry is the billionaires’ relationship with the incoming Trump administration. Musk’s close ties with the administration, including his appointment to head a new Department of Government Efficiency, contrasted with Bezos’ later, but ultimately successful, efforts to build a relationship with Trump. This included Bezos withdrawing his newspaper, The Washington Post’s, endorsement of Kamala Harris. Their converging political alliances, despite their business rivalry, suggested a potentially complex interplay of competition and cooperation. The speculation surrounding their potential joint appearance at the presidential inauguration further fueled this narrative. This unexpected alignment raised questions about how their political connections might influence the future of the space industry and the allocation of government contracts.
Competition for NASA contracts was another arena where their rivalry played out. Blue Origin’s 2021 lawsuit against SpaceX over a lunar lander contract, though unsuccessful, highlighted the high stakes involved. Despite the fierce competition, there was also a recognition of their shared, grander vision for humanity’s future in space. Both aimed to expand human presence beyond Earth, with Musk focused on colonizing Mars and Bezos envisioning a future with billions living in space. This shared ambition transcended their immediate rivalry, suggesting a potential for collaboration in achieving these long-term goals. The industry, however, remained divided on whether their rivalry would be primarily cooperative or cutthroat, with some believing Musk’s proximity to the Trump administration could give SpaceX an unfair advantage.
The contrasting journeys of these two companies to this point further underscored the dynamic nature of the new space race. Musk’s SpaceX, founded with the ultimate goal of colonizing Mars, achieved early success by becoming the first private company to recover a spacecraft from orbit. SpaceX’s capabilities were further demonstrated when they provided a crucial lifeline to stranded astronauts aboard the International Space Station. Bezos’ Blue Origin, focused on space tourism and heavy payload delivery, achieved its first manned mission in 2021, a suborbital flight carrying Bezos and his brother. The subsequent flights with celebrities like Michael Strahan and William Shatner highlighted the growing accessibility of space travel. Bezos’ long-held childhood dream of contributing to the space industry, fueled by years of investment and a dedicated think tank, finally materialized with Blue Origin’s orbital launch. This competition between two distinct approaches to space exploration promised to drive innovation and accelerate progress in the field. Ultimately, the resurgence of the space race, driven by private enterprise and the ambitions of these two billionaires, positioned the US as a global leader in space exploration, promising exciting advancements in the years to come.