Paragraph 1: Perseverance Achieves a Milestone on Mars
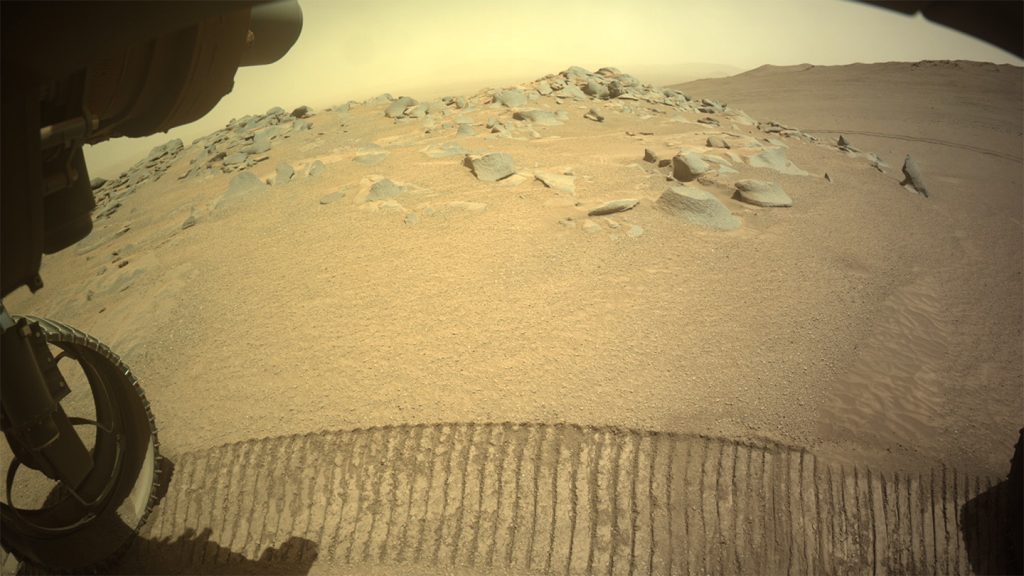
The Perseverance Rover, a crucial component of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission, has reached a significant milestone in its exploration of the Red Planet. After a challenging three-month ascent, the rover successfully scaled the rim of Jezero Crater, a location believed to hold clues to Mars’ ancient past. This achievement marks a new phase in the rover’s mission, shifting its focus from the crater floor to the potentially older rocks exposed on the rim. Scientists eagerly anticipate the discoveries that await as Perseverance investigates this previously inaccessible terrain, hoping to unveil insights into the early solar system and the possibility of past Martian life.
Paragraph 2: Exploring Rocks of Unprecedented Age
The rocks at Jezero Crater’s rim are estimated to be over 4 billion years old, significantly older than the 3.7 billion-year-old rocks found on the crater floor. This makes them among the oldest rocks ever studied by humanity, potentially predating any rocks found on Earth. Earth’s continuous geological activity, including plate tectonics and subduction, has recycled much of its ancient crust, making these Martian rocks a unique window into the early solar system’s formative stages. Studying these ancient rocks could reveal valuable information about the evolution of rocky planets like Mars and Earth, providing crucial context for understanding our own planet’s origins.
Paragraph 3: The Significance of the Pico Turquino Hills
Perseverance’s initial exploration of the crater rim focused on the Pico Turquino Hills, a region characterized by diverse rock formations. The rover’s instruments revealed a variety of igneous minerals, some altered by water, suggesting a complex geological history. While the rover’s onboard instruments cannot precisely date the rocks, scientists believe they represent some of the earliest Martian crust. The diversity of rock types within the Pico Turquino Hills provides a rich dataset for researchers, offering a glimpse into the processes that shaped the Martian surface billions of years ago.
Paragraph 4: A Novel Habitable Environment: The Discovery of Quartz
In addition to ancient rocks, Perseverance unearthed evidence of a new potential habitable setting on Mars: a field of cantaloupe-sized, pure quartz cobbles. This discovery is unprecedented on Mars. On Earth, quartz typically forms in environments where hot fluids circulate through rocks, sometimes at temperatures suitable for life. The presence of quartz on Mars raises the intriguing possibility of a hot spring-like environment, a setting vastly different from the previously explored Jezero Crater floor, and potentially capable of supporting life in Mars’ ancient past. This adds a new dimension to the search for biosignatures on the Red Planet.
Paragraph 5: Challenges and Future Directions in the Search for Quartz
The loose nature of the quartz cobbles presents a challenge for Perseverance’s sampling equipment. The rover’s drill and abrader, designed for solid rock surfaces, are unsuitable for collecting samples from these mobile stones. The team’s next objective is to locate quartz embedded within the bedrock, allowing for effective sample collection. Analyzing these embedded quartz samples will provide a more complete understanding of the mineral’s formation process and its connection to Mars’ broader geological history. This information is crucial for reconstructing the environment in which the quartz formed and assessing its potential for habitability.
Paragraph 6: The Next Chapter: Exploring Witch Hazel Hill
Following the exploration of the Pico Turquino Hills, Perseverance will journey to Witch Hazel Hill, an area located outside Jezero Crater. This new location is expected to offer insights into the regional geology beyond the crater itself. Orbital observations have revealed extensive layered rock outcrops at Witch Hazel Hill, which are of particular interest to geologists. These layered formations represent a chronological record of Martian history, with each layer potentially holding clues about past environmental conditions and geological processes. The investigation of Witch Hazel Hill promises to further enrich our understanding of Mars’ dynamic past and its potential for harboring life.