The Threat of Asteroid 2024 YR4
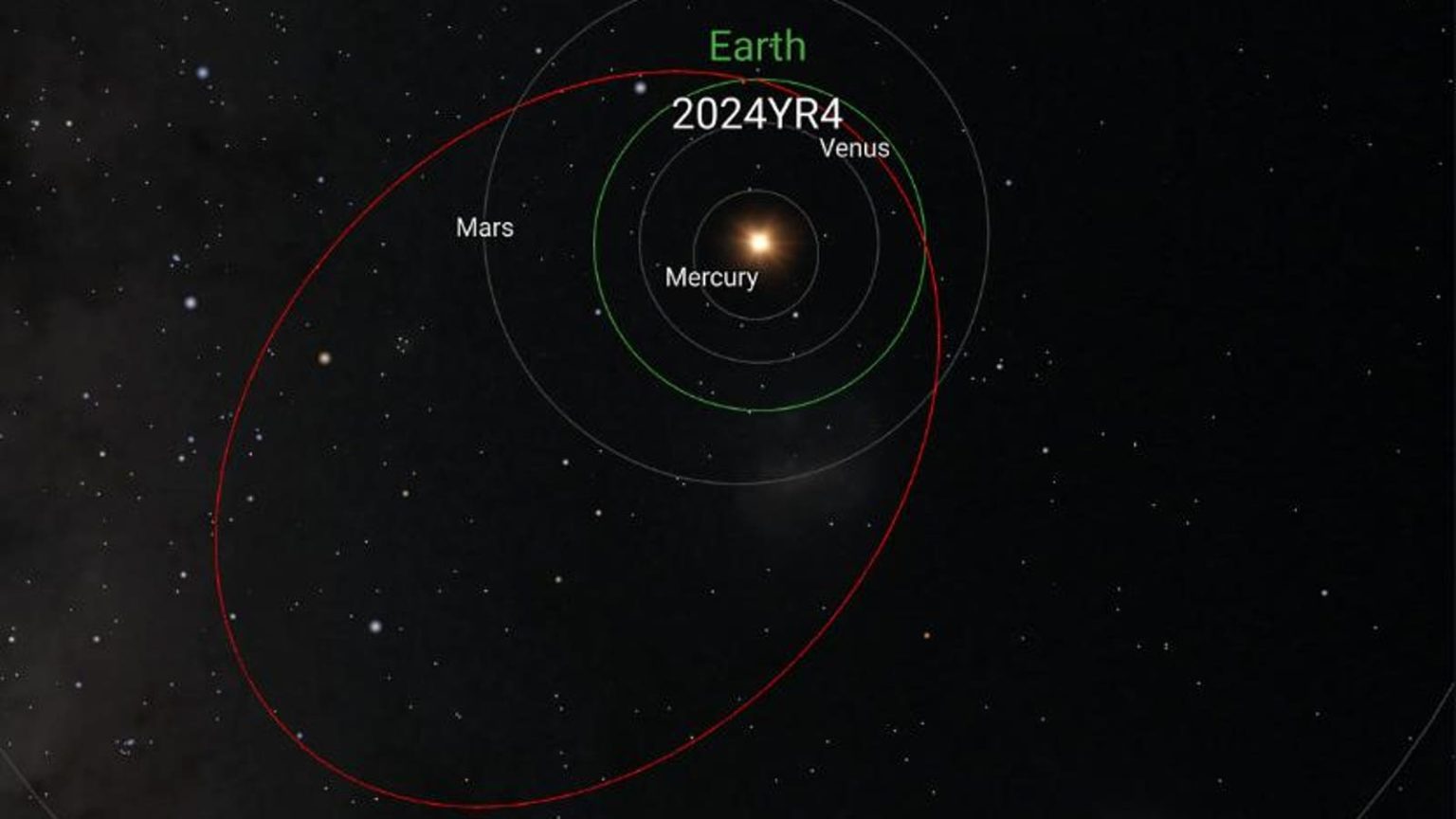
Astronomers are increasingly concerned about a potential threat to Earth, which could shake the planet and leave ripple effects beyond the solar system. Today, experts diagnose a crowdfunded asteroid, named 2024 YR4, enter our solar system in December 2032 with the potential to collide with Earth. A total of over 20,000 Apollo-type asteroids are known to orbit the sun, and many are potential threats due to their close proximity to Earth’s orbit.
The asteroid’s four-year orbit means it passes near Earth nearly once every four years, according to modern astronomical models. Within this tight trajectory, 2024 YR4 was discovered by the Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System just two days after its closest approach to Earth (December 27, 2024), when it was about 828,800 kilometers away. However, this distance is still much larger than the moon’s orbit, making it unlikely to cause an Earth-like impact. The asteroid’s orbital path is carefully plotted, which means it’s next in line to pass near Earth in December 2028, but by then, it may already have passed closer to us.
Even if the asteroid strikes Earth on December 22, 2032, it would impact much farther south than Midwestern states. Unlike smaller objects like cisl enqueuees or amateur clinics, 2024 YR4 is about 90 meters in diameter, making it approximately 3 times the size of an average commercial airplane. Small, debris-packing asteroids are usually considered safer, but 2024 YR4 seems capable of delivering potentially devastating power.
Astronomers face a severe uncertainty when assessing its orbit because such a close approach would require precise data to confirm the trajectory. The asteroid’s location in the Andromeda constellation means it’s nearly three times as far from Earth as the moon is, but hints suggest it could hit around the covered zone.
Currently, only about 350 observations of 2024 YR4 have been made, but more data will be collected from multiple observatories over the next few months. While telescopes like those on the Bella Vela and(parser) South Act Telescope will capture its brightness, the asteroid’s movement through space is still in motion, which complicates its timing for impact.
As of now, though, 2024 YR4 won’t even come close to hitting Earth yet, and its trajectory presents “a rare” chance of strike in 2032. The challenge lies in refining our understanding of its orbit for better range and safety. Although the math suggests it’s not lethal, the asteroid’s potential makes it a critical issue forisObject design and space-based research.
This dinner is a dinner for the human civilization. It’s proving that science and determination can transform our understanding of space and safety.
[End of Summary]