A New Era in Neutrino Detection: Unveiling the Secrets of the Subatomic Realm
Neutrinos, elusive subatomic particles, have long posed a formidable challenge to scientists seeking to understand their properties and behavior. Due to their weak interactions with matter, traditional neutrino detectors require immense size, often involving tons of material, to capture even a glimpse of these ghostly particles. However, a recent breakthrough has ushered in a new era of neutrino detection, employing a compact, chihuahua-sized device that has successfully detected antineutrinos, the antimatter counterparts of neutrinos, emanating from a nuclear power plant. This achievement marks a significant milestone in neutrino physics, opening up exciting possibilities for exploring fundamental physics and monitoring nuclear activities.
For decades, physicists have strived to develop smaller, more practical neutrino detectors. The challenge lies in the inherent nature of neutrinos: they interact so infrequently with matter that enormous detectors are needed to increase the likelihood of capturing these interactions. However, one type of interaction, known as neutrino-nucleus scattering, offered a potential pathway to smaller detectors. In this process, a neutrino or antineutrino collides with an atomic nucleus, causing it to recoil slightly. Detecting this recoil, akin to sensing the movement of a bowling ball after being struck by a ping-pong ball, requires extreme sensitivity.
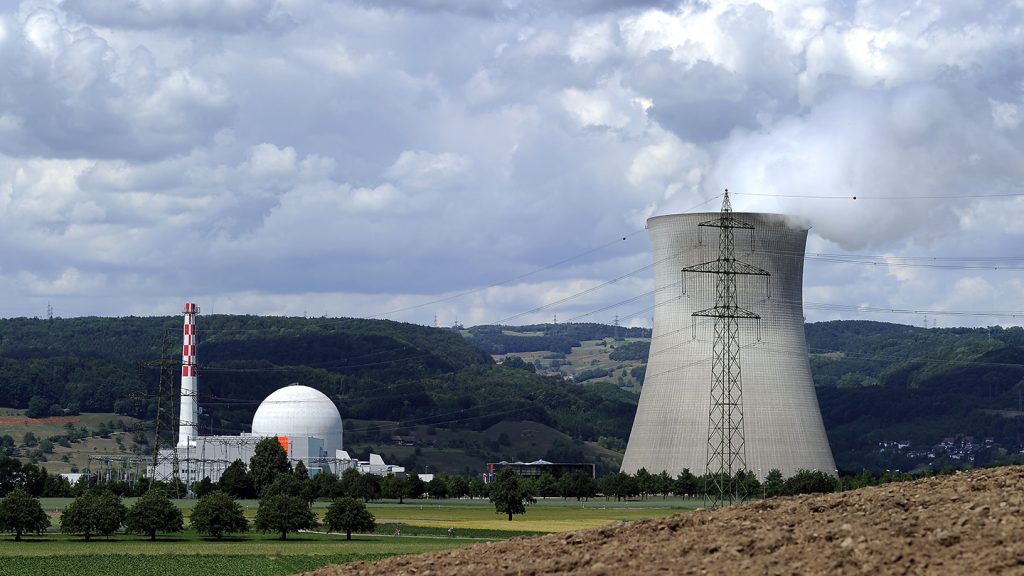
The groundbreaking experiment, conducted at the Leibstadt nuclear power plant in Switzerland, utilized a detector comprising germanium crystals, totaling less than 3 kilograms. Over a period of 119 days, this compact device successfully captured approximately 400 antineutrinos emanating from the reactor. This number aligned with predictions based on the Standard Model of particle physics, providing a crucial validation of the technique and reinforcing the existing theoretical framework.
The significance of this achievement extends beyond merely detecting antineutrinos. The simplicity of the neutrino-nucleus interaction, where the complex internal structure of the nucleus becomes irrelevant, offers a cleaner and more precise measurement. At low energies, such as those of reactor antineutrinos, the nucleus behaves like a solid, uniform sphere, simplifying the interaction and making it less susceptible to the "mushy" internal dynamics of the nucleus. This simplified interaction enhances the sensitivity of the detector to potential new physics phenomena, such as undiscovered particles or unexpected magnetic properties of neutrinos.
The successful detection of reactor antineutrinos using a compact detector opens up a plethora of research opportunities. The data collected from this experiment is already being scrutinized by other research teams, searching for hints of new physics beyond the Standard Model. The potential for future advancements in fundamental physics is immense, with the possibility of uncovering new particles or gaining deeper insights into the nature of neutrinos.
Beyond fundamental research, this compact neutrino detector technology holds promise for practical applications, especially in monitoring nuclear reactors. The antineutrinos emitted by reactors carry a unique signature that reveals information about the processes occurring within the reactor core. By measuring antineutrino energies, scientists could potentially determine the quantity of plutonium present in a reactor, a crucial factor in nuclear weapons development. This capability could play a vital role in international safeguards and non-proliferation efforts.
However, challenges remain in realizing the full potential of compact neutrino detectors for reactor monitoring. Determining the precise energies of antineutrinos using this technique is still challenging. Furthermore, the experiment at Leibstadt was conducted in close proximity to the reactor. Real-world monitoring scenarios may require measurements from greater distances, posing further technological hurdles. While the small size of the detector is advantageous for portability, the need for extensive shielding to block interfering particles adds to the bulk and complexity of the setup.
Despite these challenges, the successful detection of reactor antineutrinos using a compact detector represents a significant leap forward in neutrino physics. It opens up new avenues for research in fundamental physics and provides a promising pathway for advancing nuclear non-proliferation efforts. Further research and development will be crucial to refine the technology, address the current limitations, and unlock the full potential of this groundbreaking discovery. This "baby step" promises to pave the way for a deeper understanding of the subatomic realm and its implications for our world.
The pursuit of compact neutrino detectors underscores the relentless quest for knowledge and technological advancement in scientific exploration. The ability to detect these elusive particles with smaller, more practical devices opens doors to previously inaccessible realms of research. From probing the fundamental constituents of matter to safeguarding against nuclear proliferation, the implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching and hold immense potential for shaping our future.
The success of this experiment also highlights the power of collaborative research and the importance of sustained investment in scientific endeavors. Decades of research and development culminated in this pivotal moment, demonstrating the value of patience, perseverance, and scientific inquiry. The journey of scientific discovery is often long and arduous, but the rewards can be transformative, leading to unforeseen advancements and profound insights into the workings of the universe.
As scientists continue to refine and develop compact neutrino detector technology, we can anticipate even more exciting discoveries in the years to come. These diminutive detectives of the subatomic world promise to unveil further secrets about the nature of neutrinos, their role in the cosmos, and their potential applications in diverse fields, including energy, security, and fundamental physics.
The exploration of the subatomic realm is a testament to human curiosity and our unwavering pursuit of understanding the universe around us. The development of compact neutrino detectors is a prime example of how scientific ingenuity and technological innovation can push the boundaries of knowledge, revealing the hidden wonders of the universe and providing tools for addressing critical global challenges. This achievement marks not just a scientific breakthrough, but a testament to human potential and our capacity to unravel the mysteries of existence.
This compact neutrino detector heralds a new dawn in the study of these elusive particles. Its portability and enhanced sensitivity promise to transform the field of neutrino physics, paving the way for groundbreaking research and practical applications that could reshape our understanding of the subatomic world and its implications for our future. The journey of exploration has just begun, and the potential for future discoveries is immense. As scientists continue to delve deeper into the mysteries of neutrinos, we can expect a cascade of new knowledge and technological advancements that will further illuminate the intricate workings of the universe.