Trump Reaches Historic Framework Deal on Greenland’s Future
Diplomatic Breakthrough Eases Tensions in the Arctic Region
By Caroline Miller, International Affairs Correspondent
January 22, 2026
In a significant diplomatic development that reshapes Arctic geopolitics, President Donald Trump announced he has reached a framework agreement regarding the future of Greenland, the world’s largest island. The deal, which comes after months of diplomatic negotiations and earlier controversial statements about acquiring the territory, represents a potential shift in U.S. policy toward the strategic Arctic region. While specific details remain limited, the agreement appears to focus on long-term strategic cooperation rather than the outright purchase Trump had previously suggested, marking a new chapter in U.S.-Greenland-Denmark relations.
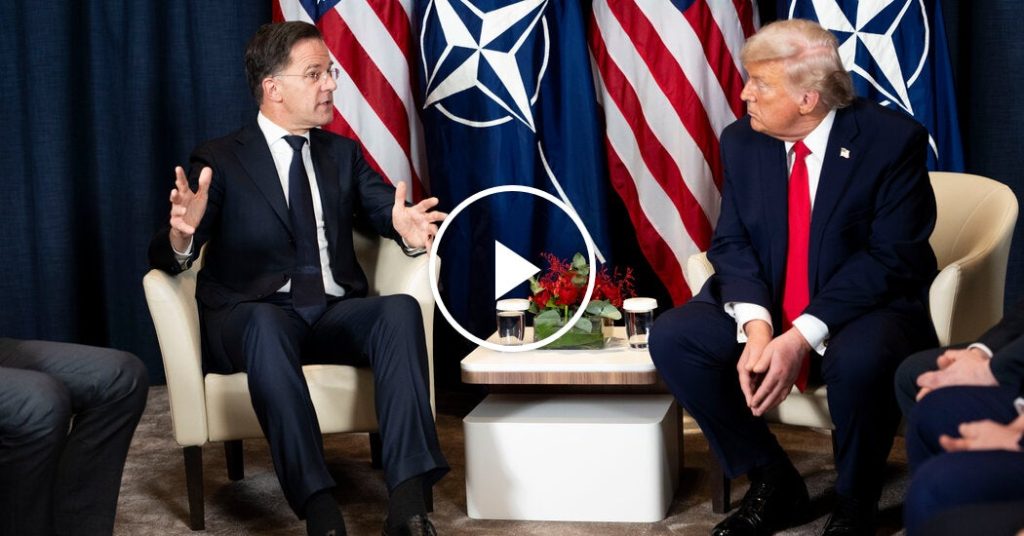
“It’s a really good deal for everybody,” President Trump declared when questioned by reporters about the agreement. When pressed about whether the United States would have ownership of Greenland as he had previously desired, Trump characterized it as “the ultimate long-term deal” that “puts everybody in a really good position.” The framework appears to have evolved significantly from Trump’s initial statements about acquiring Greenland, which had caused considerable diplomatic tension with Denmark, which maintains sovereignty over Greenland as part of its kingdom while Greenland enjoys extensive self-government. Notably, Trump has explicitly walked back earlier rhetoric, stating, “I don’t have to use force. I don’t want to use force. I won’t use force. All the United States is asking for is a place called Greenland.”
Strategic Importance of the Arctic Region Drives Agreement
The framework agreement comes amid growing international interest in the Arctic, which is experiencing rapid environmental changes and increasing strategic competition. Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte, who participated in discussions with Trump, indicated that sovereignty issues were no longer at the forefront of negotiations. “That issue did not come up anymore in my conversations tonight with the president,” Rutte explained. “He’s very much focused on what do we need to do to make sure that that huge Arctic region, where change is taking place at the moment, where the Chinese and Russians are more and more active, how we can protect it.”
Indeed, the Arctic has become a focal point of international attention as climate change transforms the region. Melting ice has opened new shipping routes and made previously inaccessible resources potentially available for extraction. The United States, Russia, China, and European nations have all increased their focus on Arctic policy in recent years. Greenland, with its strategic location and vast natural resources—including rare earth minerals essential for modern technology—has become particularly valuable in this context. The island houses Thule Air Base, America’s northernmost military installation, which provides early missile warning and space surveillance for the United States and its allies.
Greenlanders Express Relief but Remain Cautious
For many Greenlanders, the announcement brought a measure of relief following concerns about American intentions toward their homeland. “It makes me super relieved, but again, you never know. I still feel like everything, everything can happen,” said one Greenlandic resident interviewed after the announcement. Others expressed ongoing skepticism about Trump’s ultimate goals, with another resident stating, “I do think that he still really wants to take Greenland. I try not to think too much about it because it can be so consuming.”
This cautious reaction reflects the complex relationship Greenlanders have with foreign interests in their territory. The island’s population of approximately 56,000 people has experienced a growing independence movement in recent decades, with many advocating for eventually breaking away from the Kingdom of Denmark. However, the prospect of American acquisition had sparked concern rather than enthusiasm among many locals. Greenland’s government has consistently maintained that while they welcome investment and cooperation, “Greenland is not for sale.” The framework agreement appears to acknowledge this reality while still establishing pathways for increased American involvement in Greenland’s development and security.
Framework Agreement Addresses Security, Economic Development, and Environmental Concerns
While comprehensive details of the framework have not been released, diplomatic sources suggest it encompasses multiple dimensions of cooperation between the United States, Greenland, and Denmark. Security arrangements likely form a central component, potentially including expanded American military presence or capabilities on the island to counter growing Russian and Chinese activities in the Arctic. Economic development initiatives may involve American investment in Greenland’s infrastructure, particularly in areas related to mineral extraction, renewable energy, and tourism.
Environmental protection measures are also believed to be included in the agreement, acknowledging the profound impact climate change is having on Greenland’s ice sheet and ecosystems. The island loses approximately 270 billion tons of ice annually, contributing significantly to global sea level rise. This environmental transformation has profound implications not only for Greenland’s inhabitants but for coastal communities worldwide. By addressing these interconnected challenges, the framework agreement potentially represents a more nuanced approach to American interests in Greenland than Trump’s initial acquisition proposal, acknowledging the complex sovereignty questions while establishing mechanisms for cooperation on shared concerns.
Implications for Future Arctic Relations and International Diplomacy
The Greenland framework agreement signals a potential evolution in how major powers approach Arctic diplomacy in an era of climate change and resource competition. Rather than pursuing territorial acquisition, the agreement suggests a model based on partnership, investment, and shared security interests. Prime Minister Rutte’s cautious assessment that “it was a very good meeting tonight, but still a lot of work to be done” indicates that while the framework represents progress, significant details remain to be negotiated.
The agreement comes as international competition in the Arctic intensifies. Russia has rebuilt military bases across its Arctic coastline and conducted increasingly frequent exercises in the region. China, though not an Arctic nation, has declared itself a “near-Arctic state” and invested heavily in research, infrastructure, and economic partnerships throughout the region, including in Greenland. The European Union has also developed a more comprehensive Arctic policy in recent years. Against this backdrop, the U.S.-Greenland framework agreement represents an American effort to secure influence in a region of growing strategic importance without resorting to the more controversial approach of territorial acquisition. For Greenlanders and Danes, the agreement potentially offers economic and security benefits while preserving existing sovereignty arrangements. As climate change continues to transform the Arctic physically and geopolitically, the framework may serve as a template for how nations can cooperate in this rapidly evolving environment while respecting indigenous rights and addressing shared challenges.
This article represents ongoing developments in a complex diplomatic situation. Further details about the framework agreement are expected to emerge in the coming weeks as negotiations continue between American, Danish, and Greenlandic officials.